¥45454.00 库存:8 举报
ABBCI858模块备件ABB
品牌:ABB
型号:ABBCI858
货期: 现货 1天内发货
联系我时,请告诉我是在易卖工控网看到的,谢谢!
联系热线: 18030177759

工业备件直营超市
![]() 6年
6年
描述5.0 服务5.0 物流5.0
——— 宝贝详情 ———
ABBCI858每套关键压缩机组配备本特利3500框架每个本特利3500框架内配置冗余的3500/15电源模块每个本特利3500框架内配置3500/22M瞬态数据接口模块(RJ45网络接口) 针对上述键相测点,每套机组的本特利3500框架内配置相应的3500/25键相模块针对上述轴振、轴位移、瓦振、及壳振测点,均须配置相应的3500/42M监测器模(如适用),上述轴承温度测点,需配置相应的3500/60、61温度监测模块,或3500/62过程量监测模
每个监测通道(轴振、轴位移和瓦振)配置D立的两个继电器输出通道;采用3500/32(4通道)或3500/33(16通道)继电器模 每个本特利3500框架内配置一个3500/92Modbus通讯网关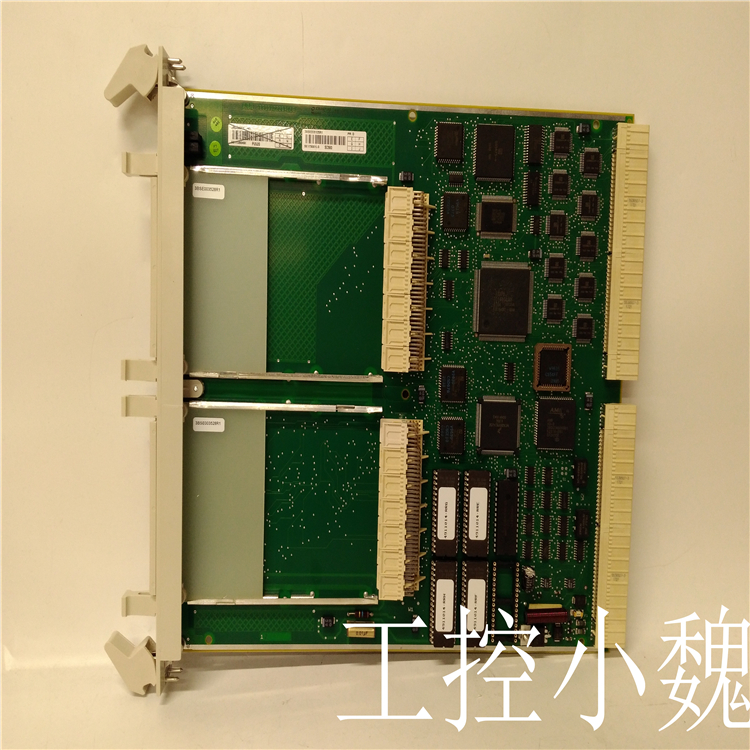


对于工作在危险区的机组,接入现场信号的3500监测器模块要带有内置安全栅;并且3500框架内要配置3500/04本安接地模块。API618往复式压缩机
对于工作在危险区域的机组,本特利传感器及监测系统都要带有多机构批准单位选项。而对于工作在安全区的机组,则不做要求。
1.测点配置要求
多事件键相:往复式压缩机的驱动端安装多事件键相转轮MEW来测量往复式压缩机的键相参考信号。该多事件键相转轮可选择本特利标准多事件转轮MEW,或者往复式压缩机生产厂家结合自己设备结构设计特点、按照本特利对于多事件键相转轮的工程实践经验来特殊定制和设计多事件键相转轮。多事件键相信号采用本特利3300XL系列电涡流传感器进行测量。
曲轴箱振动:在往复式压缩机曲轴箱两个气缸列之间的每个主轴承的水平轴线上配置一个振动速度传感器测量曲轴箱体振动。当往复式压缩机的工作转速高于500rpm时采用本特利330500系列Velomitor压电式振动速度传感器;当工作转速低于500rpm时采用本特利190501VelomitorCT压电式振动速度传感器。
十字头振动:在往复式压缩机每个气缸十字头运动中点位置的垂直平面上配置冗余的加速度传感器来监测往复运动部件的冲击事件;采用本特利330425加速度传感器进行测量。
活塞杆位置:在往复式压缩机每个气缸垂直于活塞杆平面的水平和垂直方向,配置一对互为垂直的活塞杆位置测点;采用本特利3300XL系列电涡流传感器进行测量。对于往复式压缩活塞杆的测量。
气缸动态压力:在往复式压缩机的每个气缸上配置两个气缸压力测点(吸气和排气),采用本特利165855气缸压力传感器进行测量。
轴承振动:往复式压缩机曲轴箱中每个主轴承配置一个速度传感器测量轴承的振动。当往复式压缩机的工作转速高于500rpm时采用本特利330500系列Velomitor压电式振动速度传感器;当工作转速低于500rpm时采用本特利190501VelomitorCT压电式振动速度传感器。
轴承温度:每个主轴承上配置温度传感器测量轴承温度。
气阀温度:在往复式压缩机气缸的每个气阀(吸气阀和排气阀)上配置温度测量阀门温度。
齿轮箱壳振(如适用):每个齿轮箱的输入和输出轴的支持轴承处各配置一对X/Y方向壳振测点;采用本特利330400系列压电式振动加速度传感器进行测量。
电动机瓦振:每个滚动支持轴承上配置两个瓦振测点(水平和垂直方向安装),采用本特利330500系列Velomitor压电式振动速度传感器进行测量。
2.本特利bently3500配置要求
每套关键压缩机组配备本特利3500框架
本特利bently冗余的3500/15电源模块
本特利bently3500/22M瞬态数据接口模块(RJ45网络接口)
每台机组的本特利3500框架内配置相应的3500/25键相模块
往复式压缩机曲轴箱振动、十字头振动、以及轴承振动振均配置相应的3500/70M监测器模块
活塞杆位置测点,需配置相应的3500/72M监测器模块
往复式压缩机气缸动态压力配置相应的3500/77M监测器模块
轴承温度和气阀温度测量点,需配置相应的3500/60、/61、/62或/65监测器模块
齿轮箱壳振和电动机瓦振,需配置相应的3500/42M监测器模块
每个监测通道配置D立的两个继电器输出通道;采用3500/32(4通道)或3500/33(16通道)继电器模块本特利bently一个3500/92Modbus通讯网关,对于工作在危险区的机组,接入现场信号的3500监测器模块要带有内置安全栅;并且3500框架内要配置3500/04本安接地模块。
本特利bently3500旋转机械振动保护仪表和状态监测系统的产品质量严格遵循美国API670标准。
本特利振动监测培训教程,本教程的主要内容:位移传感器噪声源
噪声是一种你不需要的信号,但多数情况下,在测量过程中,噪声是无法避免的。尽管在测量过程中无法除噪声,但可以将噪声降低到Z小程度,使其不影响你对信号的分析。要做到这一点,就要了解噪声的来源和特征。噪声是一种不合乎需要的信号成分,它可以歪曲数据,妨碍你从数据中提取机器状态信息的能力,包含的信息与机器的状态无关。噪声可以从测量系统的一个环节引入振动信号,但系统各个部分对噪声的敏感程度不同。本特利位移传感器包括bently3300系列的涡流传感器探头。
位移传感器噪声源
1·安装:传感器支架振动5、偏差(runout)–机械偏差
位移传感器噪声源
偏差(runout)–电偏差合金元素不均匀导电性不均匀导磁性不均匀轴材料局部应力集中轴上存在局部磁化区域
位移传感器噪声源
偏差(runout)与运行时间–短时间机械偏差和电偏差是稳定的
位移传感器噪声源
偏差(runout)与运行时间–中等时间热力参数和工艺参数发生变化位移传感器噪声源
偏差(runout)与运行时间–长时间某些噪声源(锈、腐蚀和局部磁化区等)发生变化
位移传感器噪声源
转子弯曲:为什么转子弯曲经常作为偏差处理,旋转的弯曲产生1X信号?机械故障诊断中,动态振动信号的1X成分是有用的。当研究机械的同步响应时,弯曲产生的信号要进行补偿,
位移传感器噪声源
转子弯曲–如果转子弯曲是0性的,就可以按1X噪声源处理–某些弯曲,是不稳定的,会随着温度和负荷变化,这类弯曲如果具有可重复性,也可以按照噪声处理。轴裂纹产生的弯曲随裂纹的扩展而变化,且不具有重复性。三个定时器都使用一个中断IRQ5。定时器中断状态寄存器用于确定哪些计时器启动了中断。中断状态寄存器是一个通用输入寄存器,位于82C54外部,位于从电源管理基输入/输出地址偏移31h。中断状态寄存器地址可以通过首先确定PCI配置基址来找到对于设备ID 7113h和供应商ID 8086h。电源管理基本输入/输出地址可以通过从此PCI配置地址读取偏移量40h来找到。计时器中断状态寄存器位位于电源管理的偏移量31h处基址输入/输出地址,位5、6和7(参见图4-2)。从电源管理基本输入/输出地址读取偏移量31h的字节用于获取这些位。位5、6和7分别对应于计时器2、1和0,为了计时器中断状态寄存器,首先将零(0)写入通用输出寄存器,位于电源管理基座的偏移37h输入/输出地址位3、4和6(不是位3、4和5)。然后将1写在相同的重新启用定时器中断状态寄存器的位。位3、4和6对应于定时器2、1和0分别使用PC/AT的标准程序定时器中断IRQ5。有关使用82C54定时器的示例,请参阅附录D。VMIVME-7698计时器从500美元开始映射到输入/输出地址空间。请参阅表4-1计时器,由三个16位计时器和一个控制字寄存器组成(见图4-4)通过8位数据总线读取/写入。定时器0、1和2这三个定时器在功能上是等效的。因此,只有
将描述单个计时器。图4-5是计时器的框图。每个计时器功能独立。尽管控制字显示在计时器块中它不是计时器的一部分,但其内容直接影响计时器的工作方式功能。如图4-5所示,当锁存时,状态寄存器包含当前控制字寄存器的内容以及输出和负载的当前状态计数标志(状态字可通过Read Back命令获得,请参阅第59页的“阅读”部分)。计时器标记为TE(计时器元素)。它是一个16位同步可预设向下柜台标记为OLM和OLL的块是8位输出锁存器(OL)。下标M和L代表0高有效字节和0低有效字节。这些插销通常跟踪TE,但在收到命令时,将锁定并保持当前计数,直到CPU读取计数。读取锁存计数时,OL寄存器将继续跟踪TE。读取OL寄存器时,必须执行两次8位访问以检索计时器的完整16位值,因为一次只启用一个锁存器。TE无法读取;从OL寄存器读取计数。A single interrupt, IRQ5, is used by all three Timers. A Timer Interrupt Status register
is provided in order to determine which Timer(s) initiated an interrupt. The interrupt
status register is a general-purpose input register located, external to the 82C54, at
offset 31h from the Power Management base I/O address. The interrupt status
register address can be found by first determining the PCI Configuration base address
for Device ID 7113h and Vendor ID 8086h. The Power Management base I/O address
can be found by reading offset 40h from this PCI Configuration address. The Timer
Interrupt Status register bits are located at offset 31h from the Power Management
base I/O address, bits 5, 6, and 7 (refer to Figure 4-2).A byte read of Offset 31h from the Power Management base I/O address is used to
obtain these bits. Bits 5, 6, and 7 correspond to Timers 2, 1, and 0, respectivelyIn order to clear the Timer Interrupt Status register, first write zeros (0’s) to the
general-purpose output register located at offset 37h of the Power Management base
I/O address bits 3, 4, and 6 (Not bits 3, 4 and 5). Then write ones (1’s) to these same
bits to re-enable the Timer Interrupt Status register. Bits 3, 4, and 6 correspond to
Timers 2, 1, and 0, respectivelyThe Timer Interrupts are cleared using the standard procedure for clearing PC/AT
IRQ5. Refer to Appendix D for an example of using the 82C54 timers.The VMIVME-7698 Timers are mapped in I/O address space starting at $500. See
Table 4-1. The Timers, consisting of three 16-bit timers and a Control Word Register
(see Figure 4-4) are read from/written to via an 8-bit data bus.The three Timers, Timer 0, 1, and 2, are functionally equivalent. Therefore only a
single Timer will be described. Figure 4-5 is a block diagram of a Timer. Each Timer is
functionally independent. Although the Control word is shown in the Timer block
diagram, it is not a part of the Timer, but its contents directly affect how the Timer现场运维工单派遣频繁,24小时ON CALL没商量?ABB助力运维法方式升级,从周期性运维到状态运维和预测性运维,预判你的预判,助你成为运筹帷幄的“全知全能”。
ABB从多年环网柜设计、制造和运行经验出发,开发出众多具有针对性的智能监测和诊断算法,用以实现设备由周期性运维到状态运维和预测性运维的转变,从而减少现场运维工单的派遣,节约人力。ABB基于真实设备数据的算法开发,大幅提高了监测诊断的准确率,更率先提出了自学习动态阈值的理念,直面设备个体差异,实现阈值的实时调整、自动调整,精准识别判断设备运行状态,让设备运维更省心夏日是度假休憩的季节,如何能顶着炎炎烈日、在设备前稳坐如钟?ABB多样化用户交互手段让你不再苦守现场一卷到底,远程亦可便捷进行信息交互,不被工作束缚远行的步伐,轻松享受盛夏。
ABB数字智能环网柜Safe Digital可以自由接入ABB Ability™ 云端平台,实现数据的远程访问,多种数据查看途径让你随时随地掌控设备情况:可通过柜体上的显示屏,查看所有设备运行数据和设备健康状态;可通过扫描二维0,使用手机连接智能终端WiFi,通过手机浏览设备监测实时数据;可搭乘“云边融合”的快车,通过ABB Ability™云端平台(或客户私有平台)查看数据情况。重要事件信息及时推送到客户订阅手机号,实现设备状态“零延时”掌握。ABB数字智能环网柜Safe Digital不仅性能优越,还在设计中考虑了易更换性,便于二次设备升级改造。通过更简单的计划和更少的改造投入实现设备全寿命周期的成本降低,全面呵护客户的资产健康,提高客户资产的投资价值。
具有出色 TFT/LED 显示颜色和多协议连接性的触摸屏面板。它们是易于使用的 HMI,具有全面和集成的模板和库,适用于您需要的每个可能的过程。
所有标准面板均配备 TFT/LED 显示屏中的高分辨率图形。大多数型号提供宽屏、高分辨率显示屏,以提高效率和出色的操作员交互。
完全可部署的 HMI,具有适用于每个可以想象的过程的全面和集成的模板和库。Panel Builder 工具具有熟悉的 Microsoft® Windows® 环境以及多语言支持,可实现快速、简单和高效的工程设计。81001-450-53-R当写入该字段时,定时器4在下一次上升时加载写入的值计时器时钟的边缘,无论计时器是启用还是禁用。这个存储在该寄存器中的值也会在终端计数时自动重新加载(或超时)。读取任一字段时,当前计数值被锁定并返回。有两种模式确定如何锁定计数,具体取决于WDT控制状态寄存器(CSR2)中的“读取锁存选择”位。参见CSR2有关这两种模式的更多信息,请注册说明。读取此字段时,当前计数值被锁定并返回。有两种模式确定如何锁定计数,具体取决于WDT控制状态寄存器(CSR2)中的“读取锁存选择”位。参见CSR2有关这两种模式的更多信息,请注册说明。定时器4电流计数寄存器(TMRCCR4)定时器4的电流计数可通过定时器4电流计数寄存器读取(TMRCCR4),位于BAR2中地址的偏移量0x28处81001-450-53-R A-B高压变频器模块
I.中央处理单元(CPU)
中央处理单元(CPU)是PLC的控制中枢。它按照PLC系统程序赋予的功能接收并
存储从编程器输入的用户程序和数据,检查电源、存储器、VO以及警戒定时器的状态,
并能诊断用户程序中的语法错误:当PLC投入运行时,首先它以扫描的方式接收现场各输
入装置的状态和数据,并分别存入IO映像区,然后从用户程序存储器中逐条读取用户程
序,经过命令解释后,按指令的规定将逻辑或算术运算的结果送入Vo映像区或数据寄存
器内。等所有的用户程序执行完毕之后,0后将1/O映像区的各输出状态或输出寄存器内
的数据传送到相应的输出装置,如此循环运行,直到停止运行为止。
为了进一步提高PLC的可靠性,近年来对大型PLC还采用双CPU构成冗余系统,或
采用三CPU的表决式系统。这样,即使某个CPU出现故障,整个系统仍能正常运行。
2.存储器
存放系统软件的存储器称为系统程序存储器。
(1) PLC常用的存储器类型。
1) RAM (Random Assess Memory)。这是-一种读/写存储器(随机存储器)其存取速
度0快,由铿电池支持。he corresponding 3500 / 72m monitor module shall be configured for the piston rod position measuring point
Reciprocating compressor cylinder dynamic pressure configuration corresponding 3500 / 77m monitor module
Bearing temperature and air valve temperature measurement points shall be equipped with corresponding 3500 / 60, / 61, / 62 or / 65 monitor modules
Corresponding 3500 / 42m monitor module shall be configured for gearbox shell vibration and motor pad vibration
Each monitoring channel is configured with two relay output channels of vertical D; The 3500 / 32 (4-channel) or 3500 / 33 (16 channel) relay module Bently is used as a 3500 / 92 Modbus communication gateway. For the unit working in the hazardous area, the 3500 monitor module accessing the field signal shall be equipped with a built-in safety barrier; And 3500 / 04 intrinsically safe grounding module shall be configured in the 3500 rack.
The product quality of Bently 3500 rotary machinery vibration protection instrument and condition monitoring system strictly complies with the American API 670 standard.
Bentley vibration monitoring training course, the main content of this course: displacement sensor noise source
Noise is a signal you don't need, but in most cases, noise is unavoidable in the measurement process. Although the noise cannot be removed during the measurement process, the noise can be reduced to a small level Z so that it will not affect your analysis of the signal. To do this, it is necessary to understand the source and characteristics of noise. Noise is an undesirable signal component, which can distort data and hinder your ability to extract machine state information from the data. The information contained is irrelevant to the state of the machine. Noise can be introduced into the vibration signal from one part of the measurement system, but each part of the system has different sensitivity to noise. Bently displacement sensors include Bently 3300 series eddy current sensor probes.
Noise source of displacement sensor
1. Installation: vibration of sensor support 5. Runout - Mechanical deviation
Noise source of displacement sensor
Runout – electrical deviation: alloy elements are non-uniform, conductivity is non-uniform, magnetic conductivity is non-uniform, local stress of the material is concentrated, and there is local magnetization area on the axis
Noise source of displacement sensor
Runout and run time – short time mechanical and electrical deviations are stable
Noise source of displacement sensor
Runout and running time - the noise source of displacement sensor when thermal and process parameters change in medium time
Runout and running time – some noise sources (rust, corrosion, local magnetization zone, etc.) change for a long time
Noise source of displacement sensor
Rotor bending: why is the rotor bending often treated as deviation, and the rotating bending generates 1x signal? The 1x component of dynamic vibration signal is useful in mechanical fault diagnosis. When studying the synchronous response of the machine,
Noise source of displacement sensor
Rotor bending – if rotor bending is permanent, it can be treated as 1x noise source – some bending is unstable and will change with temperature and load. If such bending is repeatable, it can also be treated as noise. The bending caused by the axial crack varies with the crack propagation and has no repeatability. All three timers use an interrupt irq5. The timer interrupt status register is used to determine which timers initiated interrupts. The interrupt status register is a general-purpose input register, which is located outside the 82C54 and offset 31h from the input / output address of the power management base. The interrupt status register address can be found for the device ID 7113h and the vendor ID 8086h by first determining the PCI configuration base address. The power management basic input / output address can be found by reading the offset 40H from this PCI configuration address. The timer interrupt status register bit is located at the base address input / output address at the offset 31h of the power management, bits 5, 6 and 7 (see Fig. 4-2). The byte of offset 31h is read from the power management basic input / output address for acquiring these bits. Bits 5, 6 and 7 correspond to timers 2, 1 and 0 respectively. For the timer interrupt status register, zero (0) is first written to the general output register, which is located at offset 37h input / output address bits 3, 4 and 6 (not bits 3, 4 and 5) of the power management base. Then write 1 to the same bit of the re enable timer interrupt status register. Bits 3, 4 and 6 correspond to timers 2, 1 and 0 respectively interrupt irq5 using the standard program timer of PC / at. See Appendix D for an example of using the 82C54 timer. The vmivme-7698 timer maps to the input / output address space from $500. Refer to table 4-1. The timer is composed of three 16 bit timers and a control word register (see Figure 4-4) and is read / written through the 8-bit data bus. Timers 0, 1 and 2 are functionally equivalent. Therefore, only
A single timer will be described. Fig. 4-5 is a block diagram of a timer. Each timer functions independently. Although the control word is displayed in the timer block, it is not a part of the timer, but its content directly affects the working mode and function of the timer. As shown in Figure 4-5, when latched, the status register contains the contents of the current control word register and the current status count flag of the output and load (the status word can be obtained through the read back command, see the "reading" section on page 59). The timer is marked te (timer element). It is a 16 bit synchronous presettable block marked as OLM and oll and is an 8-bit output latch (OL). Subscripts m and l represent the most significant byte and the least significant byte. These pins usually track te, but when a command is received, they lock and hold the current count until the CPU reads the count. When the latch count is read, the ol register will continue to track te. When reading the ol register, you must perform two 8-bit accesses to retrieve the full 16 bit value of the timer because only one latch is enabled at a time. Te cannot be read; Read the count from the ol register. A single interrupt, IRQ5, is used by all three Timers. A Timer Interrupt Status register
is provided in order to determine which Timer(s) initiated an interrupt. The interrupt
status register is a general-purpose input register located, external to the 82C54, at
offset 31h from the Power Management base I/O address. The interrupt status
register address can be found by first determining the PCI Configuration base address
for Device ID 7113h and Vendor ID 8086h. The Power Management base I/O address
can be found by reading offset 40h from this PCI Configuration address. The Timer
Interrupt Status register bits are located at offset 31h from the Power Management
base I/O address, bits 5, 6, and 7 (refer to Figure 4-2). A byte read of Offset 31h from the Power Management base I/O address is used to
obtain these bits. Bits 5, 6, and 7 correspond to Timers 2, 1, and 0, respectivelyIn order to clear the Timer Interrupt Status register, first write zeros (0’s) to the
general-purpose output register located at offset 37h of the Power Management base
I/O address bits 3, 4, and 6 (Not bits 3, 4 and 5). Then write ones (1’s) to these same
bits to re-enable the Timer Interrupt Status register. Bits 3, 4, and 6 correspond to
Timers 2, 1, and 0, respectivelyThe Timer Interrupts are cleared using the standard procedure for clearing PC/AT
IRQ5. Refer to Appendix D for an example of using the 82C54 timers. The VMIVME-7698 Timers are mapped in I/O address space starting at $500. See
Table 4-1. The Timers, consisting of three 16-bit timers and a Control Word Register
(see Figure 4-4) are read from/written to via an 8-bit data bus. The three Timers, Timer 0, 1, and 2, are functionally equivalent. Therefore only a
single Timer will be described. Figure 4-5 is a block diagram of a Timer. Each Timer is
functionally independent. Although the Control word is shown in the Timer block
Diagram, it is not a part of the timer, but its contents directly affect how the timer on-site operation and maintenance work orders are dispatched frequently, and 24-hour on call is not discussed? ABB helps to upgrade the operation and maintenance method, from periodic operation and maintenance to state operation and maintenance and predictive operation and maintenance, to predict your prediction and help you become a "omniscient and omnipotent" strategist.
Based on years of experience in the design, manufacturing and operation of ring network cabinets, abb has developed many targeted intelligent monitoring and diagnosis algorithms to realize the transformation of equipment from periodic operation and maintenance to state operation and maintenance and predictive operation and maintenance, so as to reduce the dispatch of on-site operation and maintenance orders and save manpower. ABB's algorithm development based on real equipment data has greatly improved the accuracy of monitoring and diagnosis. It also took the lead in putting forward the concept of self-learning dynamic threshold, directly facing the individual differences of equipment, realizing real-time adjustment and automatic adjustment of threshold, accurately identifying and judging the operating status of equipment, and making equipment operation and maintenance more worry free. Summer is a holiday and rest season. How can you stand in front of the equipment in the scorching sun? ABB's diversified user interaction means make you no longer have to wait on the site to the end. Remote information interaction can also be carried out conveniently, and you can easily enjoy the midsummer without being bound by work.
安全提示:
请勿随意接收任何来源不明的文件,请勿随意点击任何来源不明的链接。涉及资金往来的事项请务必仔细核对资金往来信息。
——— 猜你喜欢 ———

ABB BAILEY IMAS123 仓库现货
型号:ABB BAILEY IMAS123
¥ 价格面议

ABB BAILEY IMMFP12 仓库现货
型号:ABB BAILEY IMMFP12
¥ 价格面议

DSDP170 57160001-ADF ABB 现货议价
型号:57160001-ADF ABB
¥ 价格面议

ABB INICT03A 现货议价
型号:ABB INICT03A
¥ 价格面议

ABB IMAS113 贝利卡件 全新现货议价
型号:ABB IMAS113
¥ 价格面议

ABB SAFT125 CHC ABB SAFT138 CHS ABB SAMC 19 INF ABB SAFT181 INF ABB SAFT189 ISI ABB SAFT160F 380 ABB
型号:ABB SAFT125
¥ 2365.00
X
¥45454.0
库存:8